M-Commerce
M (Mobile) Commerce is the E Commerce through mobile devices.
M-Commerce vs E-Commerce
| M-Commerce |
E-Commerce |
| It stands for Mbile Commerce. |
It stands for Electronic Commerce. |
| It uses mobile devices for commercial transactions. |
It uses computers for commercial transactions. |
| It is not limited to location specific. |
It needs to go to a place where there is Internet access to computer. |
| It is very handy and easy to carry. |
It is not easy to always carry your pc or laptop. |
| It is always reliable and easy to access. |
It is not always reliable |
| It is costly compared to E commerce. |
It is economical and low priced. |
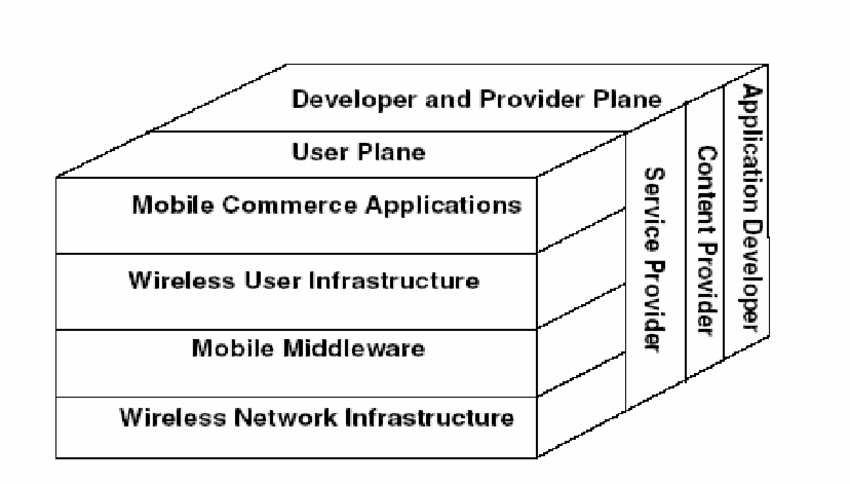
M-Commerce Framework
It is a framework that is used to develop mobile commerce applications. It is a set of components that are used to develop mobile commerce applications.
The authors identified two planes of reponsibility :
User Plane
It is responsible for the interaction between the user and the system. It is divided into four layers :
- M Commerce Applications : These are the applications that enable users to engage in commercial transactions using mobile devices.
- Wireless User Interface : It is the user interface layer that allows users to interact with the mobile commerce system through wireless devices.
- Wireless Middleware : It is the layer that provides communication and integration services between the mobile commerce applications and the wireless network infrastructure.
- Wireless Network Infrastructure : It is the underlying network infrastructure that enables wireless communication and connectivity for mobile commerce applications.
Provider Plane
It is responsible for the interaction between the system and the service providers. It is divided into three layers :
- Network Services Providers : These are the providers that offer wireless network services to mobile commerce applications.
- Applications Service Providers : These are the providers that offer mobile commerce applications to users.
- Content Applications Service Providers : These are the providers that offer content and services to mobile commerce applications.
Issues in M Commerce
There are several issues that need to be addressed in order to make M Commerce successful. Some of the key issues are :
- Security Issues: These refer to the potential threats and vulnerabilities that could compromise the security of a mobile commerce application. This includes issues like data breaches, unauthorized access, fraud, malware, and other cyber threats that could impact the confidentiality, integrity, or availability of the application or its data.
- Wireless Infrastructure Issues: These refer to the challenges and limitations of the wireless network infrastructure that supports mobile commerce applications. This includes issues like network coverage, bandwidth, latency, reliability, and scalability that could impact the performance and user experience of the application.
- Usability Issues: These refer to the design and usability challenges of mobile commerce applications. This includes issues like user interface design, navigation, accessibility, responsiveness, and user experience that could impact the usability and adoption of the application by users.
- Ethical Issues: These refer to the ethical considerations and implications of mobile commerce applications. This includes issues like data privacy, consent, transparency, fairness, accountability, and social responsibility that could impact the ethical use and impact of the application on individuals and society.
- Legal Issues: These refer to the legal requirements and regulations that govern mobile commerce applications. This includes issues like data protection, consumer rights, intellectual property, liability, and compliance that could impact the legal obligations and responsibilities of the application developers, providers, and users.
- Privacy Issues: These refer to the privacy concerns and risks associated with mobile commerce applications. This includes issues like data collection, tracking, profiling, monitoring, and sharing that could impact the privacy and confidentiality of the user's personal information and data.
Applications of E-Commerce
- E-Shopping: This refers to buying and selling goods and services online. Websites like Amazon and eBay are examples of e-shopping platforms.
- E-Marketing: This involves using digital media platforms to market products and services. This includes email marketing, social media marketing, and search engine marketing.
- E-Banking: This refers to the use of electronic systems to perform banking activities such as money transfers, checking account balance, paying bills, etc.
- E-Learning: This involves using electronic technologies to access educational curriculum outside of a traditional classroom. Websites like Coursera and Udemy are examples of e-learning platforms.
- Online Auction: This refers to the process of buying and selling goods or services by offering them up for bid and then selling the item to the highest bidder. eBay is a well-known example of an online auction platform.
- Online Portals: These are web-based platforms that provide employees, customers and suppliers with a single point of access to information.
- E-Real Estate: This refers to the buying, selling, and renting of property online. Websites like Zillow and Realtor.com are examples of e-real estate platforms.
- E-Publishing: This involves the digital publication of e-books and electronic articles, and the development of digital libraries and catalogues.
E-Commerce and Retail Industry
E-Commerce has provided opportunity for retailers to gain potential customers, improve communications, etc. It has made their stores a secondary option. With E-Commerce, shops will be able to sell their products 24/7 while keeping their costs at a minimum. It can also prevent over staffing because E-Commerce will be its own sales person.
E-Governance
E Governance use Information and Communication Technology (ICT) to improve the quality of delivering government services, exchange of information, etc. It can be defined as the delivery of government services and information to the public.
The importance of E-Governance can be seen in building strong and effective information chain. The rational of e governance is in its need in reducing red tape, promotion of knowledge, fulfiling expectations of people, etc.
Stages
- Computerization: This is the first stage of e-governance where the government departments are computerized and the data is stored in digital form.
- Networking: This is the second stage where the government departments are connected through a network to share information and resources.
- Online Presence: This is the third stage where the government departments have an online presence through websites and portals to provide information and services to the public.
- Online Interactivity: This is the fourth stage where the government departments interact with the public online through e-services, e-forms, and other online applications.
Challenges
- Lack of integrated services
- Population
- Clarity about objective
- Misconception about information transparency
- Localization
- Budget
- Security threats and legal issue
- Maximum use of infrastructure
- Standardization
Cyber Law
Cyber law concentrates on creating compliance regulations for organization to protect clients and their data. Cyber law is the law governing the use of computers and the internet. It is the set of framework, some rules and guidelines that define certain business activities.
Cyber law encompasses laws relating to :
- Cyber crime : It encompasses any criminal act dealing with computers and networks (called hacking). It can be defined as Offences that are committed against individuals or groups of individuals with a criminal motive to intentionally harm the reputation of the vitim or cause physical or mental harm to the victim directly or indirectly using modern networks or technologies.
- Electronic and digital signatures : Authentication of any electronic record by a subscriber by means of an electronic method or procedure.
- Intellectual property : It means legal term and refers to patents, copyright, trademarks, etc.
- Data protection and privacy : It refers to set of privacy laws, policies, and procedures that aim to minimize intrusion into one's privacy caused by the collection, storage and dissemination of personal data.
Cyber Crime
It can be defined as Offences that are committed against individuals or groupds of individuals with a criminal motive to intentionally harm them.
The cyber criminals can be distinguished on the basis of their skill levels and motivations :
- Novice : They are beginners having limited computer and programming skills.
- Cyberpunks : They are capable of writing their own software and have understanding of systems. Many are engaged in credit card number and telecommunicaiton fraud.
- Internals : Those people who have been either fired by their employer or are dissatisfied with their employer.
- Petty thieves : Those include employees, contractors, consultatnts who are computer literate and motivated by greed or neessity to pay off their habits.
Spoofing
Spoofing is a type of cyber attack in which a hacker disguises themselves as a trusted entity to gain unauthorized access to sensitive data or information. This can be done through email spoofing, IP address spoofing, or website spoofing.
There are several types of spoofing attacks, including :
- Email Spoofing: This involves sending emails that appear to be from a legitimate source, such as a bank or government agency, in order to trick the recipient into revealing sensitive information or clicking on malicious links.
- Caller ID Spoofing: This involves manipulating the caller ID information displayed on a phone to make it appear as though the call is coming from a trusted source, such as a local business or government agency.
- URL Spoofing: This involves creating fake websites that mimic the appearance of legitimate websites in order to trick users into entering their login credentials or other sensitive information.
Phishing
Phishing is a type of cyber attack in which a hacker attempts to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card numbers, by posing as a legitimate entity in an electronic communication. This can be done through email phishing, SMS phishing, or voice phishing.
Sniffing
Sniffing is a type of cyber attack in which a hacker intercepts and monitors network traffic to capture sensitive information, such as usernames, passwords, and credit card numbers, as it travels across the network. This can be done through packet sniffing, network sniffing, or wireless sniffing.
Denial of Service (DoS) Attack
A Denial of Service (DoS) attack is a type of cyber attack in which a hacker floods a network, system, or website with traffic in order to overwhelm it and make it unavailable to legitimate users. This can be done through volumetric attacks, protocol attacks, or application layer attacks.
There are several types of DoS attacks, including :
- Buffer Overflow: This involves sending more data to a program than it can handle, causing it to crash or become unresponsive.
- Ping of Death: This involves sending oversized or malformed packets to a target system, causing it to crash or become unresponsive.
- Smurf Attack: This involves sending spoofed ICMP echo requests to a network's broadcast address, causing all hosts on the network to respond to the target system, overwhelming it with traffic.
- Syn Flooding: This involves sending a large number of TCP SYN packets to a target system, causing it to become overwhelmed and unable to respond to legitimate traffic.
- Teardrop: This involves sending fragmented IP packets with overlapping payloads to a target system, causing it to crash or become unresponsive.
Cyber Forensics
Cyber forensics is the process of collecting, analyzing, and preserving digital evidence in order to investigate and prosecute cyber crimes. It involves using specialized tools and techniques to recover data from computers, networks, and other digital devices, and to trace the source of a cyber attack or security breach.
Investigation and Surveillance
It includes interviewing, surveillance, search and seizure and formal legal process mechanisms.
Basic steps necessary when conducting the cyber crime investigation are :
Interview, Search and Seize
Investigation authorities often engage in personal interviews, questioning involved parties to gather as much information as possible about the case.
Search and Seize is an active mode of investigation, which involves discovering evidence, identifying suspects, apprehending offenders and interviewing witnesses.
Surveillance
Surveillance is the monitoring of activities, behavior, or information for the purpose of gathering intelligence, preventing crime, or ensuring security. In the context of cyber forensics, surveillance may involve monitoring network traffic, tracking user activities, or observing digital communications to gather evidence and identify potential cyber criminals.
Forensics
Once they have gathered enough information through interviews and surveillance, investigators will get warrants to collect targeted computers for advanced forensic analysis. It involves mining a computer and unearthing potential evidence.
Undercover
It may require investigators to go undercover, adopting fake online personae to trap criminals.
Cyber Crimes and Information Act 2000
In 1999, the government of India realised the need for introducing a new law to deal with the technology in the field of cyber crimes. In May 2000, both the houses of the Indian Parliament passed the Information Technology Bill.
Cyber crimes is not defined officially in IT Act or in any other legislation. Offence or crime has been dealt with elaborately listing various acts and punishments for each under the Indian Penal Code.
The concept of cyber crim is just a combination of crime and computer.
Scope
It covers to whole of India. This act can also be operated to any offences or contravention committed outside India by any person irrespective of his nationality.
Objective
The objective of the Information Technology Act of 2000 is to provide a legal framework for dealing with technology-related crimes and to facilitate electronic commerce. It aims to address the growing concerns of cybercrime and establish provisions for the security and protection of electronic data and information. The act also aims to promote the use of digital signatures and electronic records, ensuring their legal validity and authenticity. Additionally, the act seeks to establish a regulatory framework for electronic governance and facilitate the development of a secure and reliable digital infrastructure in India.
Chapters
It is based on UNCITRAL (United Nations Commission on International Trade Law) Model Law. It has 13 chapters, 94 sections and 4 schedules
- Chapter 1 : Commencement, application and definitions
- Chapter 2 : Authentication of electronic records through digital signature
- Chapter 3 : Electronic Governance
- Chapter 4 : Attribution, Acknowledgement and Dispatch of Electronic Records
- Chapter 5 : Secure Electronic Records and Secure Digital Signatures
- Chapter 6 : Regulation of Certifying Authorities
- Chapter 7 : Digital Signature Certificates
- Chapter 8 : Duties of Subscriber
- Chapter 9 : Penalties, Compensation and Adjudication
- Chapter 10 : The Cyber Appellate Tribunal
- Chapter 11 : Offences
- Chapter 12 : Network Service Providers Not to be Liable in Certain Cases
- Chapter 13 : Miscellaneous provisions
Offences and Cyber Crimes under IT Act 2000
-
Tampering with computer source documents
- Description: Altering, destroying, or manipulating computer source code with the intent to cause damage.
- Penalty: Imprisonment up to three years or a fine up to two lakh rupees or both.
-
Hacking with computer system
- Description: Unauthorized access to computer systems or networks with the intent to cause damage or steal information.
- Penalty: Imprisonment up to three years or a fine up to five lakh rupees or both.
-
Receiving stolen computer or communication device
- Description: Receiving or possessing a stolen computer or communication device knowing or having reason to believe it to be stolen.
- Penalty: Imprisonment up to three years or a fine up to one lakh rupees or both.
-
Using password of another person
- Description: Unauthorized use of a password, digital signature, or any other unique identification feature of another person.
- Penalty: Imprisonment up to three years or a fine up to one lakh rupees or both.
-
Cheating using computer resource
- Description: Using a computer resource to cheat or deceive someone.
- Penalty: Imprisonment up to three years or a fine up to one lakh rupees or both.
-
Publishing private images of others
- Description: Publishing or transmitting images of a person’s private areas without their consent.
- Penalty: Imprisonment up to three years or a fine up to two lakh rupees or both.
-
Acts of cyber terrorism
- Description: Any act that threatens the unity, integrity, security, or sovereignty of India or its relations with other countries.
- Penalty: Imprisonment ranging from imprisonment for life to rigorous imprisonment up to ten years and fine.
-
Publishing images containing sexual acts
- Description: Publishing or transmitting obscene material containing sexual acts.
- Penalty: Imprisonment up to three years or a fine up to five lakh rupees or both.
-
Failure to maintain records
- Description: Failure to maintain records as required by law or regulation.
- Penalty: Fine which may extend to Rs. 25,000 for the first contravention and Rs. 50,000 for the second or subsequent contravention.
-
Misrepresentation
- Description: Making a false representation to obtain any computer service.
- Penalty: Imprisonment up to three years or a fine up to one lakh rupees or both.
Conclusion
In this chapter, we explored the various applications of E-Commerce, from e-shopping and e-banking to e-learning and online auctions. We also discussed the role of mobile technology in E-Commerce and the security issues that can arise in this context. As we've seen, E-Commerce is a vast and rapidly evolving field that offers numerous opportunities for businesses and consumers alike, but it also presents significant challenges in terms of security and privacy. In the next chapter, we'll delve deeper into these challenges and explore strategies for mitigating them.